Anne: The Chapter Book Collection – adapted by Kallie George, illustrated by Abigail Halpin
Tundra Books, 2025
Anne Dares – adapted by Kallie George, illustrated by Abigail Halpin
Tundra Books, 2023

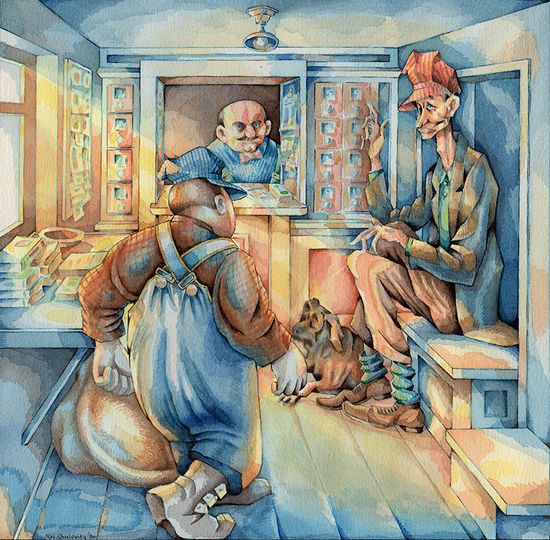
For fans of Kallie George and Abigail Halpin’s wonderful collaboration in bringing the work of Lucy Maud Montgomery to chapter book readers, Tundra has issued a boxed set of paperback editions. As you will read on my earlier posts (see here and here and here and here), this series is both an accessible introduction to the original Anne of Green Gables, and each volume a wonderful illustrated novel that stands on its own merits. Abigail Halpin’s pictures offer her own perspective on the characters and setting, and Kallie George has succeeded in writing an homage to Montgomery’s vision, not a bland imitation.

In Anne Dares, the bold aspect of Anne Shirley’s personality propels her to take some risks. These include the physically daring walking on the edge of a fence, as well as the courage to perform in her school’s recital. The fence-walking stunt even requires her to ignore the advice of kindred spirit Diana. Ever conscious of a dramatic situation, Anne assures her friend, “And if I do perish,…you can have my pearl-bead ring.

Her performance involves facing her apparent nemesis, Josie Pye, as well as Gilbert Blythe, the boy whose thoughtless teasing will prove to be a mere mask over his true feelings. Her new puff sleeved dress, a gift from her beloved father figure, Matthew, gives her some of the strength she needs in front of an audience. The dress is both a cherished article of clothing, as well as a tangible proof of the love that now characterizes her home life, although her initial arrival had provoked skepticism. On stage, at first “she thought she might faint.” Daring or not, she is still afraid. Fortunately, “she knew she must live up to those puffed sleeves.” Montgomery’s heroine, re-imagined by Kallie George and Abigail Halpin, lives in two worlds, where undeniable difficulties and dreams of beauty are intertwined.